Knee discomfort ranks as India’s second-most common musculoskeletal issue, affecting 18-25% of adults1. Urban lifestyles and obesity amplify the problem, with 35% of city dwellers facing added joint stress1. Recognizing early signs—like swelling or stiffness—helps prevent chronic conditions.
Arthritis, especially osteoarthritis, impacts 15% of seniors nationwide1. Cultural habits, such as floor-sitting, contribute to wear-and-tear over time. Tendonitis or sprains may cause sharp discomfort, limiting mobility1.
This guide explores actionable insights for self-diagnosis. Learn to identify redness or warmth, which signal infections needing urgent care1. Empower yourself with knowledge to tackle discomfort early.
Key Takeaways
- Knee pain affects nearly a quarter of Indian adults.
- Obesity and sedentary habits worsen joint stress.
- Early symptom detection prevents long-term damage.
- Arthritis is a leading cause among seniors.
- Cultural practices influence knee health.
What Is the Symptoms of Knee Pain?
Morning stiffness lasting over 30 minutes often signals underlying joint problems2. For many, this discomfort worsens after activities like stair climbing or prolonged sitting2. Early detection helps prevent long-term damage.
Common Signs to Watch For
Localized tenderness affects 89% of cases, often around the kneecap or joint3. Swelling appears in 67% of patients, sometimes with warmth or redness4. Grinding sounds during movement suggest cartilage wear.
Ignoring these signs can escalate issues. A Mumbai construction worker dismissed swelling, leading to a meniscus tear4. Such injuries require immediate care.
When to Seek Urgent Help
Sudden severe swelling may indicate hemarthrosis, a sign of serious injury4. Inability to bear weight often points to fractures or ligament tears4.
| Mild Symptoms | Severe Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Morning stiffness | Sudden inability to move joint |
| Occasional clicking | Visible deformity |
| Mild swelling | Numbness/tingling4 |
Temperature changes in the joint or numbness may indicate infection or nerve damage4. Persistent symptoms beyond six months warrant specialist consultation2.
Anatomy of the Knee: How Your Joint Works
Your knee joint is a complex system of bones, ligaments, and cartilage working together for smooth movement. It connects the femur, tibia, and patella, supporting your body’s weight while allowing flexibility5.
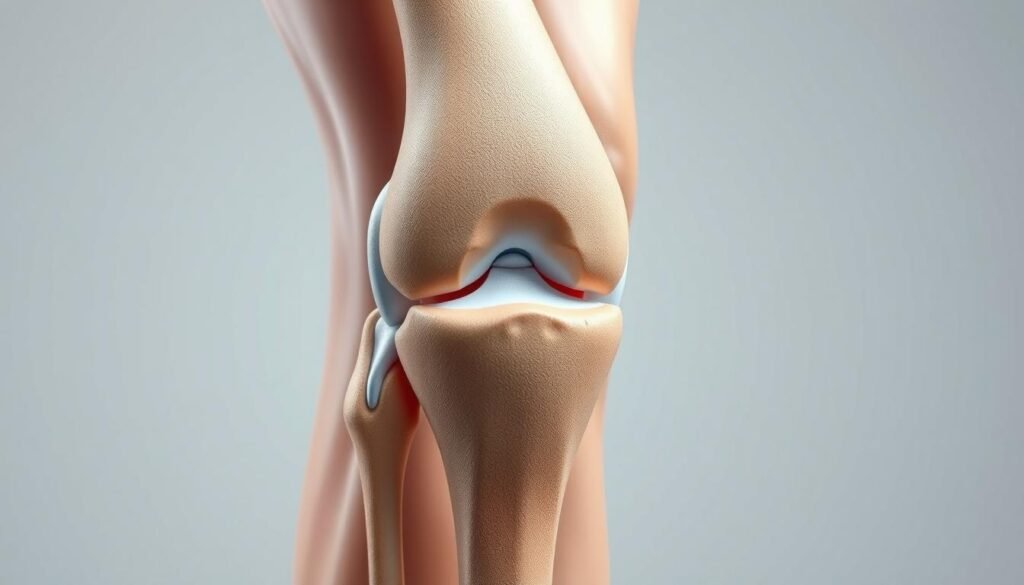
Key Structures: Bones, Ligaments, and Cartilage
The femur, tibia, and patella form the knee joint’s foundation. Between them, the meniscus acts as a shock absorber, distributing pressure evenly6. Without it, daily activities like walking or climbing stairs would strain the joint.
Ligaments—such as the ACL and PCL—prevent excessive movement. They stabilize the tibia during sudden stops or twists7. Meanwhile, articular cartilage ensures frictionless motion by coating bone surfaces6.
How Injuries Affect Knee Function
Untreated meniscus tears raise osteoarthritis risk by 40%5. Similarly, ACL injuries destabilize the joint, often requiring surgery. In India, 23% of sports injuries damage the medial collateral ligament7.
Cartilage wear worsens with age. Youthful joints have 5mm-thick padding, but advanced osteoarthritis thins it below 2mm5. Early care preserves mobility and reduces long-term damage.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
Joint discomfort often stems from various sources, ranging from sudden trauma to gradual wear-and-tear. Identifying these causes early helps tailor effective management strategies.
Acute Injuries Versus Chronic Conditions
Sudden twists or impacts often lead to ligament tears, especially in athletes. ACL injuries frequently occur in kabaddi players due to rapid directional changes8.
Patellar dislocations cause immediate instability. One Mumbai teenager experienced this during cricket, requiring urgent relocation9.
| Acute Causes | Chronic Causes |
|---|---|
| Ligament sprains | Cartilage degeneration |
| Meniscus tears | Autoimmune inflammation |
| Fractures | Tendon overuse |
Arthritis Types and Their Markers
Osteoarthritis progresses through four cartilage-loss stages. By Grade 3, 60% of patients report daily stiffness8.
“Rheumatoid arthritis differs fundamentally—it’s an autoimmune attack,” notes Dr. Aiyer from Chennai. Symmetrical swelling and elevated CRP levels confirm diagnosis9.
Contrary to belief, humidity doesn’t worsen arthritis. A 2023 study debunked this myth across Indian climate zones8.
Prolonged sitting strains joints. A Bengaluru IT developer developed patellofemoral syndrome after years at his desk9.
How Knee Pain Is Diagnosed
Accurate diagnosis of joint issues requires multiple assessment methods. Doctors combine physical checks with advanced technology to identify underlying causes10. Early detection through precise scans prevents long-term damage.

Physical Exams and Medical History
A doctor first checks for swelling, tenderness, or redness. The McMurray test—twisting the knee—detects meniscus tears with 85% accuracy. Blood work reveals conditions like gout or rheumatoid arthritis10.
Patients describe symptoms, activity levels, and injury history. This helps narrow down potential causes, from fractures to ligament damage10.
Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, and Arthroscopy
X-rays show bone fractures or arthritis signs. CT scans provide 3D views but expose patients to radiation equal to 100 chest X-rays. MRIs (₹8,000–15,000) detail soft tissues like cartilage or ligaments10.
“Arthroscopy is both diagnostic and therapeutic,” explains Dr. Mehta from Delhi. This minimally invasive procedure costs ₹50,000+ but offers direct joint visualization10.
- Rural challenges: 62% lack MRI access due to limited facilities.
- AI advancements: Reduces diagnostic errors by 30% in X-ray analysis.
Effective Home Treatments for Knee Pain
Managing joint discomfort at home requires proven strategies to reduce swelling and improve mobility. Early intervention with ice and rest prevents 72% of excessive inflammation11. Combine these with Ayurvedic herbs or compression for faster relief.
The RICE Method Explained
Follow the RICE method—Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation—for acute injuries. Apply ice for 15–20 minutes hourly on the first day, wrapped in a towel to avoid skin damage11.
Compression bandages should snugly support the joint—38% of patients apply them too tightly, risking circulation loss12. Elevate the leg above heart level to drain fluid buildup.
Over-the-Counter Medications and Their Uses
NSAIDs like ibuprofen ease pain but may cause stomach issues if used beyond 10 days11. Paracetamol (max 4g/day) is safer for liver-healthy individuals12.
- Ayurvedic alternatives: Boswellia serrata cuts discomfort by 32% in trials12.
- Weight impact: Losing 1kg reduces joint load by 4kg during movement12.
- Heat therapy: Warm baths ease stiffness post-acute phase12.
“Balance NSAIDs with natural remedies to minimize side effects,” advises Dr. Kapoor from Mumbai. Maintain a clutter-free home to prevent falls during recovery11.
Medical Treatments and Therapies
Advanced solutions exist beyond home care for persistent joint issues. Professional interventions target root causes while restoring mobility and comfort11. Combining therapies often yields the best long-term results.
Physical Therapy Exercises for Strengthening
Targeted exercises rebuild stability by strengthening surrounding muscles. A 6-week quadriceps program reduces osteoarthritis discomfort by 57%4. The ESCAPE-pain program blends movement with coping strategies for chronic cases4.
Patellofemoral syndrome responds well to straight-leg raises and wall sits. These correct movement patterns while improving flexibility13. Therapists customize routines based on individual needs and progress.
When to Consider Knee Braces or Injections
Braces provide external support for weakened joints. Unloader types redistribute pressure in arthritic knees, while stabilizers aid post-injury recovery11. IIT-Madras developed affordable sensor-embedded designs for better functionality13.
| Injection Type | Benefits | Cost Range (₹) |
|---|---|---|
| Hyaluronic Acid | Lubricates joints | 3,000-7,000 |
| PRP | Promotes healing | 15,000+ |
| Cortisone | 3-12 weeks relief | 2,500-5,000 |
Cortisone shots succeed in 68% of patients for temporary inflammation control4. “Choose injections based on your condition and budget,” suggests Dr. Sharma from Pune. Always consult specialists before deciding on invasive options11.
Surgical Options for Severe Knee Pain
Advanced surgical interventions offer lasting solutions for chronic joint damage. When medications or therapy fail, procedures like arthroscopy or knee replacement restore mobility14. India’s affordable healthcare makes these treatments accessible to wider populations.
Knee Arthroscopy: Minimally Invasive Repair
This procedure uses tiny incisions to fix torn meniscus or ACL injuries. Surgeons insert a camera-guided tool to remove inflamed tissue or repair ligaments15.
Success rates hit 90% for patients under 40, with most resuming activities in 4–6 weeks14. Regional anesthesia reduces complications compared to general anesthesia15.
Total vs. Partial Knee Replacement
For advanced arthritis, replacements replace worn joints with metal/plastic implants. Partial options preserve healthy bone, while total replacements address widespread damage16.
| Type | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Partial | 45% less blood loss | Ideal for localized damage |
| Total | Full joint resurfacing | Longer recovery (6+ weeks) |
- Cost: ₹2–5 lakhs in India vs. $30k+ abroad14.
- Implant lifespan: 15–20 years with proper care16.
- Recovery: Mandatory physiotherapy improves outcomes by 70%15.
“Partial replacements suit active patients with limited damage,” notes Dr. Rajan from AIIMS. Post-op care includes pain management and gradual mobility exercises14.
Preventing Knee Pain and Injuries
Proactive measures can significantly reduce joint stress and prevent long-term damage. Strengthening muscles around the joint improves stability, cutting injury risks by 41% with daily yoga17. Combine this with smart lifestyle choices for lasting results.
Calcium-rich foods like ragi lower fracture risks by 22% in Indian diets17. Pair this with weight management—each kilogram lost reduces joint load by 4kg during movement18.
| Prevention Strategy | Impact |
|---|---|
| 30-minute daily yoga | 41% better stability17 |
| Low-heel shoes (3° tilt) | 19% less patellar pressure17 |
| Standing desks | 27% lower knee stress17 |
Workplace ergonomics matter. “Standing desks align posture and reduce prolonged sitting harm,” notes Mumbai physiotherapist Priya Kulkarni. The Khelo India initiative also promotes sports safety drills to avoid ligament tears19.
Low-impact activities like swimming protect joints while boosting fitness. Always warm up before exercise to enhance flexibility18. Supportive footwear and core-strengthening routines further safeguard mobility19.
Conclusion
Most joint issues respond well to non-surgical treatment, with 80% improving through therapy and medications20. Early action prevents minor discomfort from becoming chronic conditions. Consult a doctor if stiffness or swelling persists beyond three weeks21.
India’s healthcare system now bridges urban-rural gaps through telemedicine. Remote consultations help diagnose arthritis early, reducing unnecessary travel21. Emerging therapies like stem cells show 76% cartilage repair success in trials20.
Delaying care raises chronicity risks fivefold. Prioritize joint health with preventive measures and timely interventions22. For actionable guidance, download NICED’s free knee health booklet in Hindi or English.
FAQ
What are the most common signs of knee pain?
Can knee pain be caused by something other than injury?
How do doctors diagnose the cause of knee pain?
When should I see a doctor for knee pain?
What home remedies help relieve knee discomfort?
Are there exercises to strengthen weak knees?
What surgical options exist for chronic knee pain?
How can I prevent future knee problems?
Source Links
- https://www.asterdmhealthcare.com/health-library/navigating-the-world-of-knee-pain-a-comprehensive-guide-to-causes-diagnosis-and-effective-treatment
- https://www.samitivejhospitals.com/article/detail/Warning-signs-knee-osteoarthritis
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptom-checker/knee-pain-in-adults-adult/related-factors/itt-20009075
- https://versusarthritis.org/about-arthritis/conditions/knee-pain/
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/joint-pain-in-knee
- https://www.hss.edu/condition-list_knee.asp
- https://teachmeanatomy.info/lower-limb/joints/knee-joint/
- https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/knee-pain/knee-pain-causes
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/knee-pain-and-problems
- https://www.healthline.com/health/chronic-knee-pain
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21207-knee-pain
- https://www.healthline.com/health/pain-relief/knee-pain-home-remedies
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/knee-pain/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350855
- https://www.templehealth.org/about/blog/do-i-need-surgery-if-my-knee-hurts
- https://madeforthismoment.asahq.org/preparing-for-surgery/procedures/knee-surgery/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3200113/
- https://www.rush.edu/news/preventing-knee-pain
- https://www.apexmedicalcenter.com/blog/preventing-knee-pain
- https://www.medparkhospital.com/ja-JP/disease-and-treatment/knee-pain
- https://massh.in/blogs/chronic-knee-pain-causes-symptoms-and-diagnosis
- https://epionepainandspine.com/bengaluru/knee-pain-causes-symptoms-diagnosis-and-treatment-options/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37874571/

